Computer systems, sub-systems and decomposition

Computer system
A computer system is made up of software, data, hardware, communications and people; each computer system can be divided up into a set of sub-systems.
Each sub-system can be further divided into sub-systems and so on until each sub-system just performs a single action.
Computer systems can be very large, very small or any size in between; most people interact with many different computer systems during their daily life without realising it.
Sub-system
In order to understand how a computer system is built up and how it works it is often divided up into sub-systems.
This division can be shown using top-down design to produce structure diagrams that demonstrate the modular construction of the system.
Each sub-system can be developed by a programmer as a sub-routine.
How each sub-routine works can be shown by using flowcharts or pseudocode.
Top-down design is the decomposition of a computer system into a set of sub- systems, then breaking each sub-system down into a set of smaller sub-systems, until each sub-system just performs a single action.
Decomposition
- Any problem that uses a computer system for its solution needs to be decomposed into its component parts.
- The component parts of any computer system are:
- inputs – the data used by the system that needs to be entered while the system is active
- processes – the tasks that need to be performed using the input data and any other previously stored data
- outputs – information that needs to be displayed or printed for the users of the system
- storage – data that needs to be stored in files on an appropriate medium for use in the future.
Construct a solution
Solutions to problems need to be designed and developed rigorously.
The use of formal methods enables the process to be clearly shown for others to understand the proposed solution.
The following methods need to be used by IGCSE Computer Science students:
- Structure diagrams
- Flowcharts
- Pseudocode
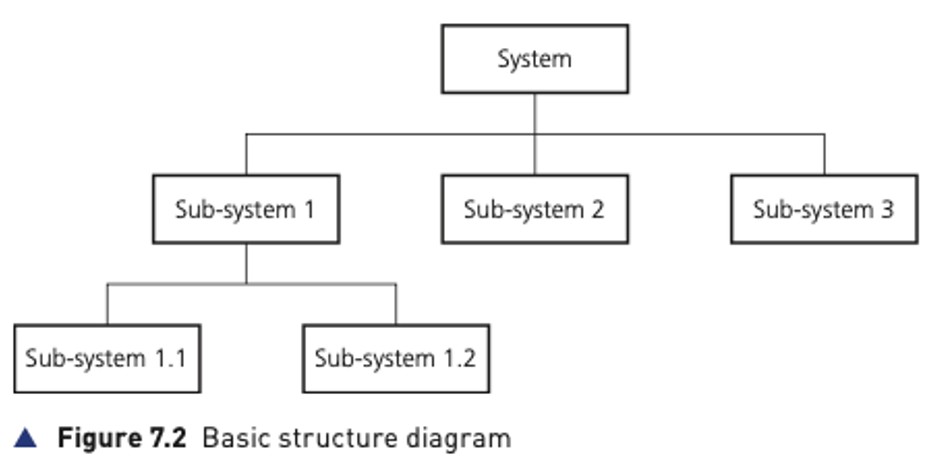
Structure diagrams
- Structure diagrams can be used to show top-down design in a diagrammatic form.
- Structure diagrams are hierarchical, showing how a computer system solution can be divided into sub-systems with each level giving a more detailed breakdown.
- If necessary, each sub-system can be further divided.
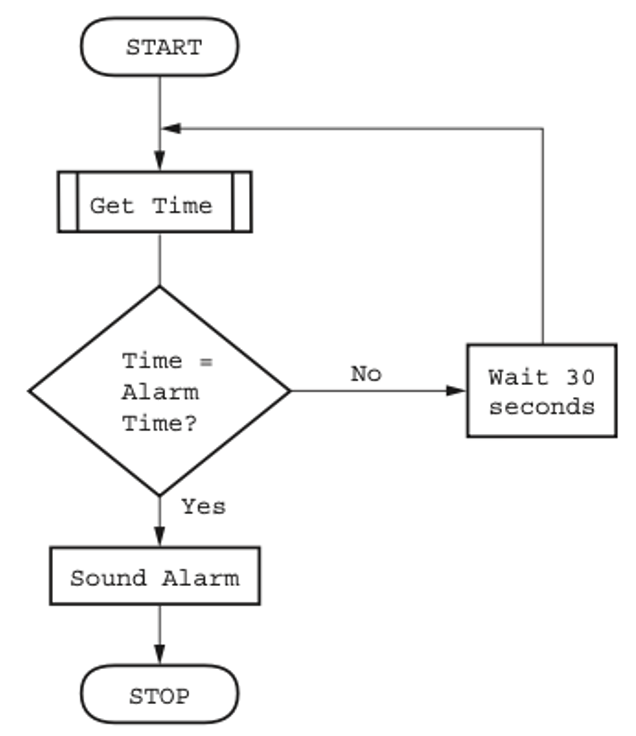
Flowchart
- A flowchart shows diagrammatically the steps required to complete a task and the order that they are to be performed.
- These steps, together with the order, are called an algorithm.
- Flowcharts are an effective way to communicate how the algorithm that makes up a system or sub-system works.
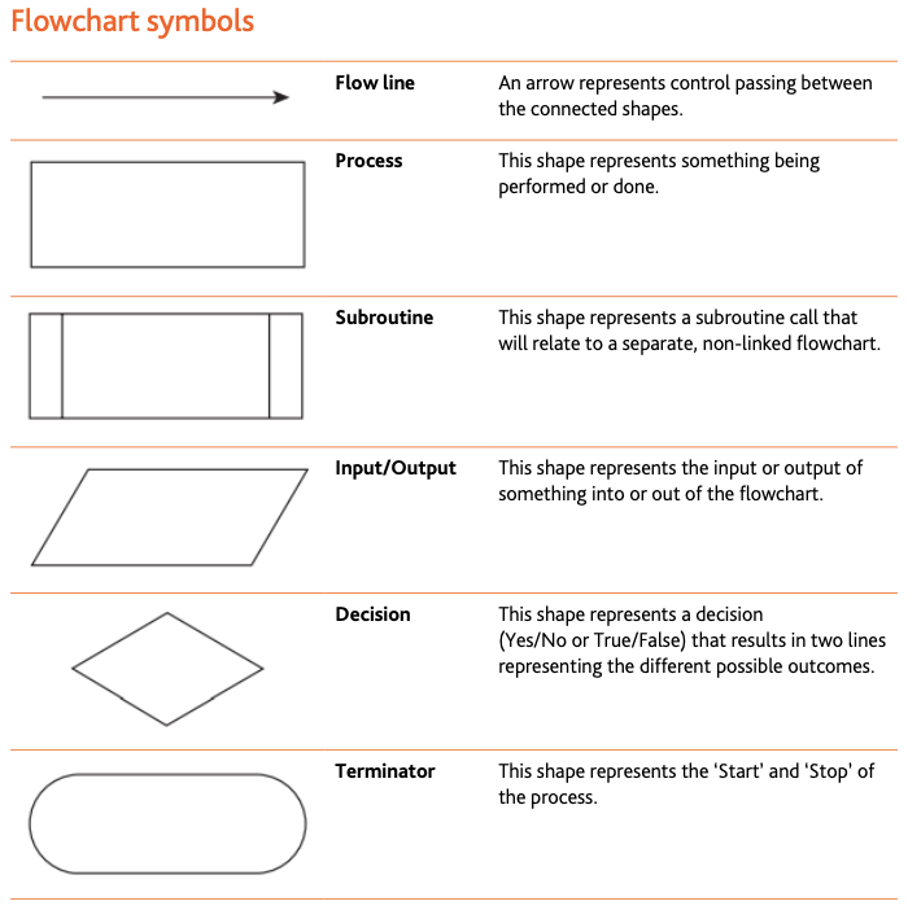
Pseudocode
- Pseudocode is a simple method of showing an algorithm.
- It describes what the algorithm does by using English key words that are very similar to those used in a high-level programming language.
- Data items to be processed by the algorithm are given meaningful names in the same way that variables and constants are in a high-level programming language.
- However, pseudocode is not bound by the strict syntax rules of a programming language.
